RESTful API
Add Query
To add a RESTful API query step to your workflow:
- Navigate to the page list and add a new workflow
- Select RESTful API from the data sources in the workflow step sidebar
- Configure your query in the input window that appears
For detailed setup instructions, see the RESTful API Data Source Guide.
Dynamic URLs
Use path variables with templates to create dynamic URLs.
{{ /users/{id}/posts }}- Replace{id}with a dynamic value{{ /organizations/{orgId}/teams/{teamId} }}- Use multiple parameters
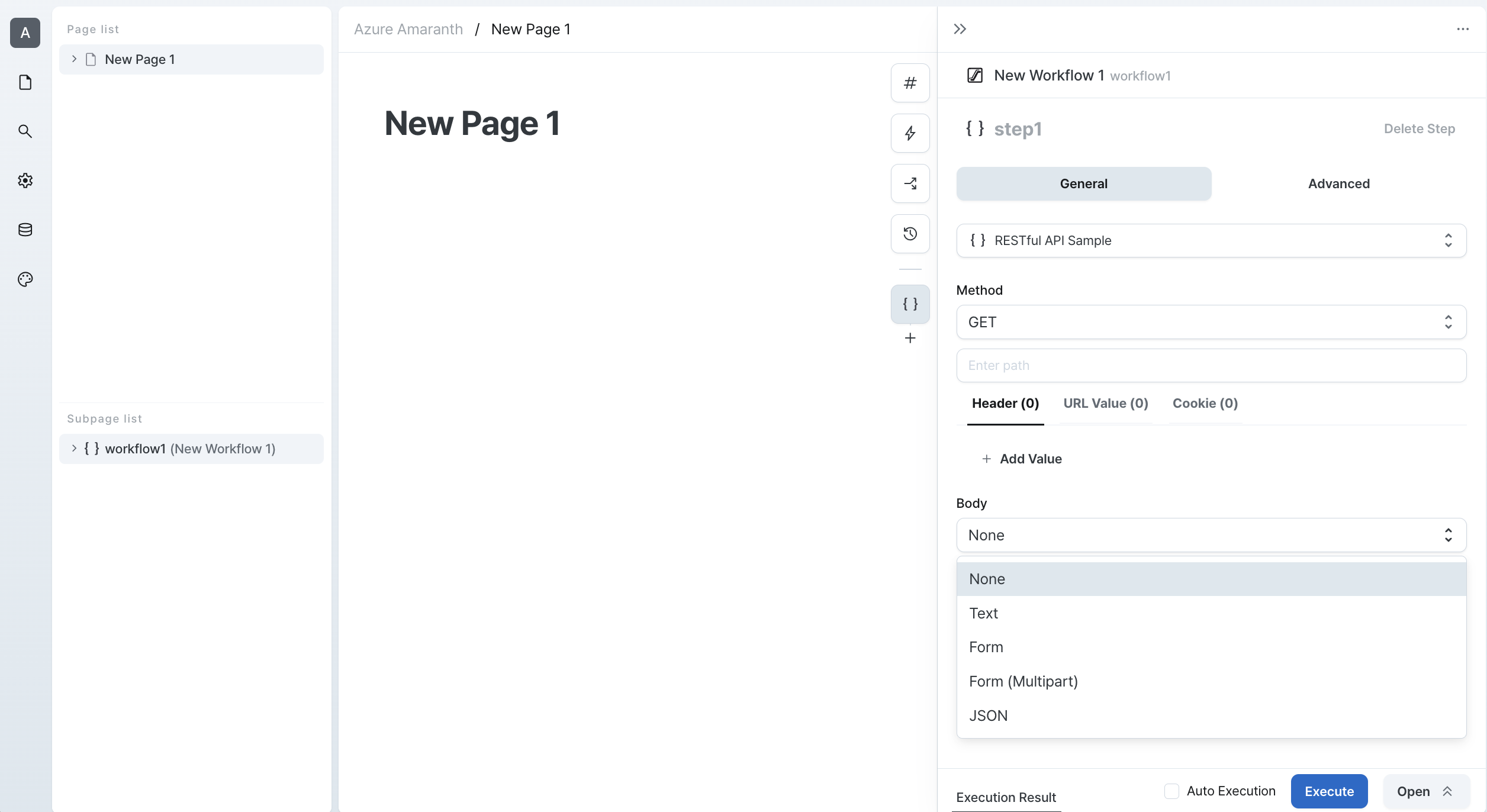
Body Formats
Choose from these supported formats:
- Text: Plain text
- Form: URL-encoded form data
- Form(Multipart): For file uploads
- JSON: JSON data
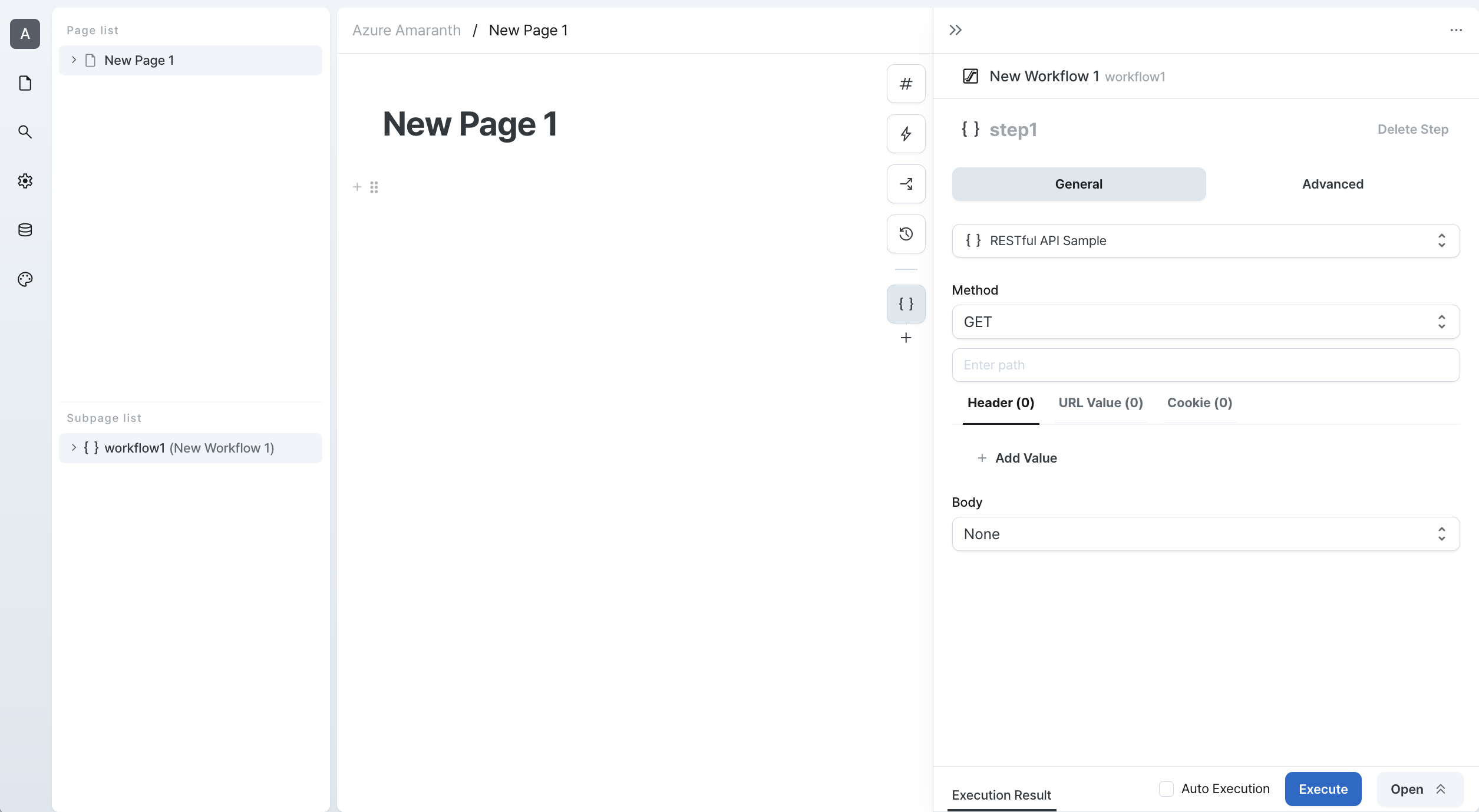
Available Methods
GET
GET requests are the most basic method for retrieving data from a server. Here's how to use GET requests:
- Specify the API endpoint URL
- Configure URL parameters and query strings as needed
- Add any required authentication headers or cookies
While GET requests typically don't include a body, you can add one if your API requires it.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Path (path) | string | API endpoint URL |
| URL Parameters (params) | object | Dynamic URL values |
| Body Type | enum | None, Text, Form, Form(Multipart), JSON |
| Body (body) | unknown | Request payload (format depends on Body Type) |
| Headers (headers) | object | HTTP headers |
| Cookies (cookies) | object | HTTP cookies |
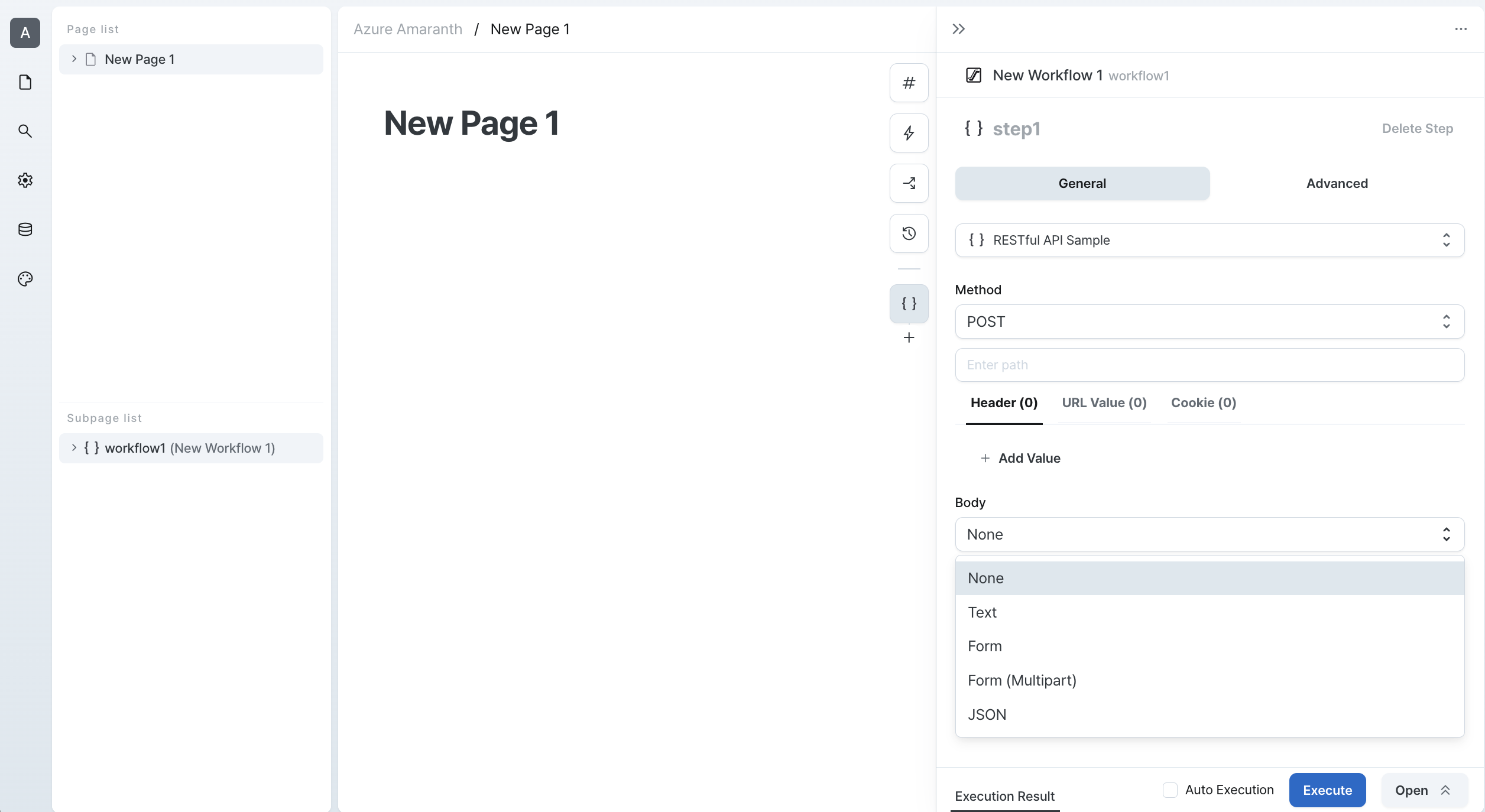
POST
POST requests are used to create new resources. Here's how to use POST requests:
- Specify the API endpoint URL
- Include the resource data in the request body
- Configure URL parameters if needed
- Select the appropriate body format
- Add any required authentication
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Path (path) | string | API endpoint URL |
| URL Parameters (params) | object | Dynamic URL values |
| Body Type | enum | None, Text, Form, Form(Multipart), JSON |
| Body (body) | unknown | Request payload (format depends on Body Type) |
| Headers (headers) | object | HTTP headers |
| Cookies (cookies) | object | HTTP cookies |
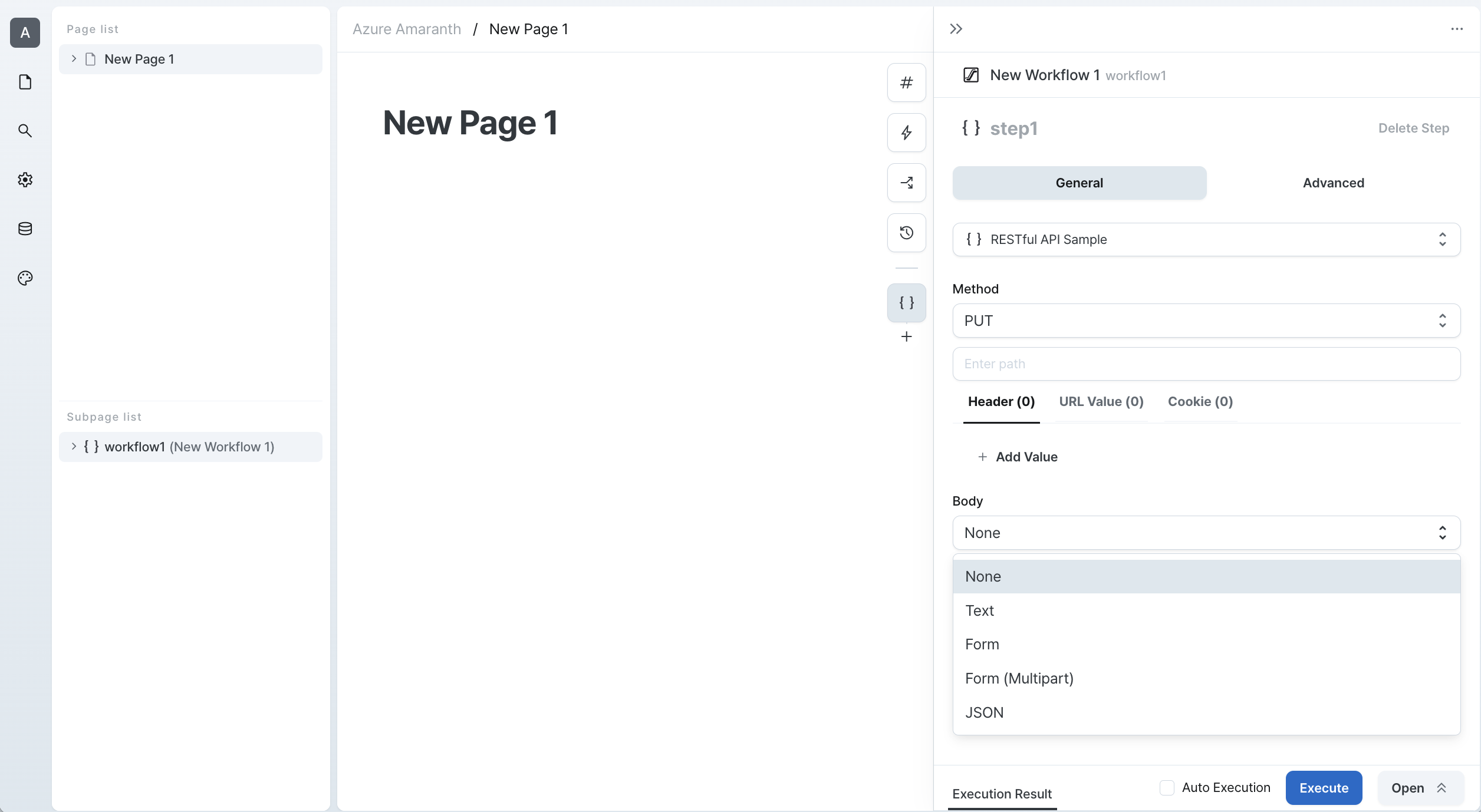
PUT
PUT requests are used to update existing resources. Here's how to use PUT requests:
- Specify the API endpoint URL
- Include the complete resource data in the body
- Configure URL parameters if needed
- Select the appropriate body format
- Add any required authentication
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Path (path) | string | API endpoint URL |
| URL Parameters (params) | object | Dynamic URL values |
| Body Type | enum | None, Text, Form, Form(Multipart), JSON |
| Body (body) | unknown | Request payload (format depends on Body Type) |
| Headers (headers) | object | HTTP headers |
| Cookies (cookies) | object | HTTP cookies |
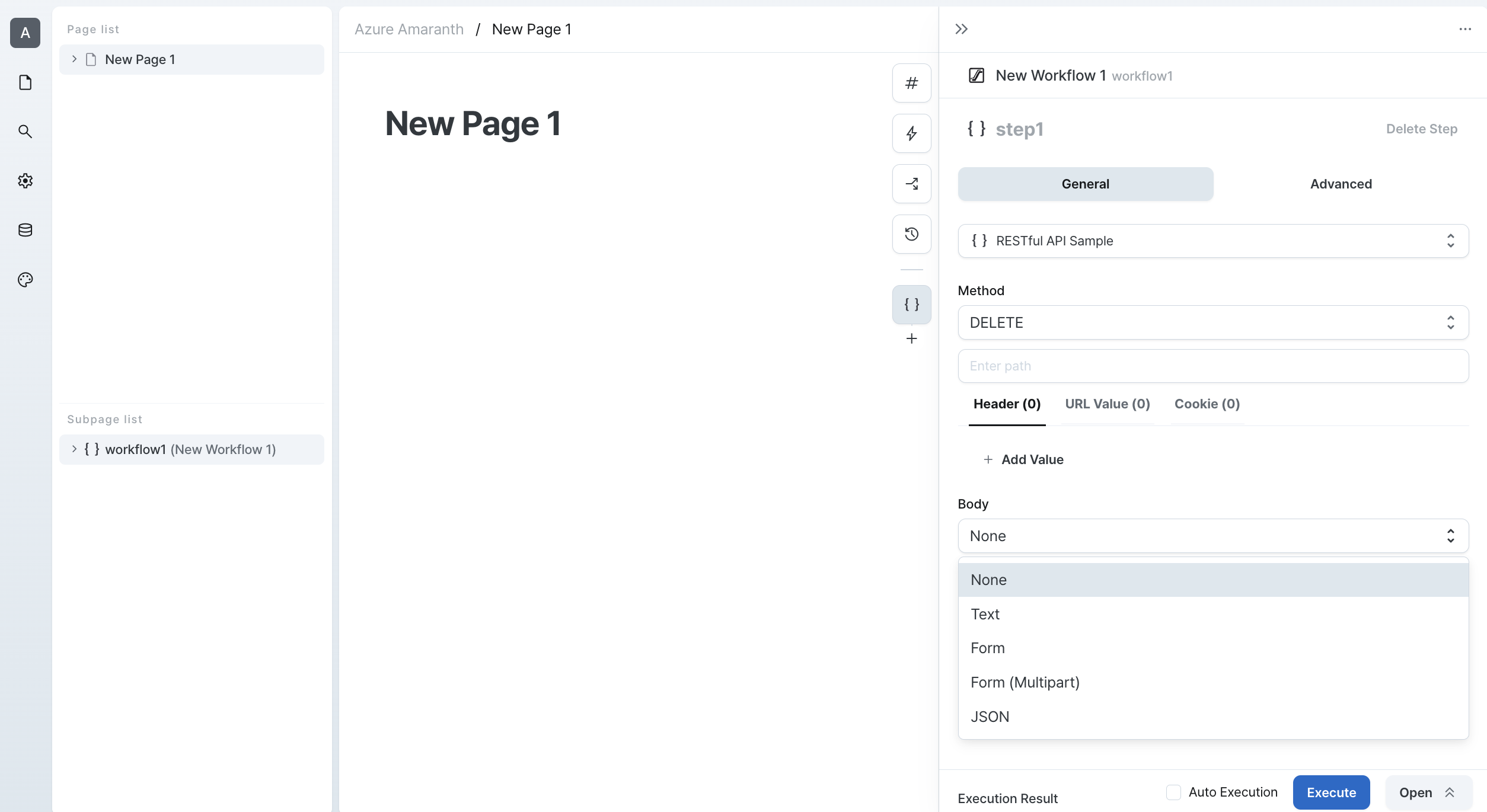
DELETE
DELETE requests are used to remove resources from the server. Here's how to use DELETE requests:
- Specify the API endpoint URL
- Include the resource identifier in the URL
- Configure URL parameters if needed
- Add any required authentication
While DELETE requests typically don't include a body, you can add one if your API requires it.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Path (path) | string | API endpoint URL |
| URL Parameters (params) | object | Dynamic URL values |
| Body Type | enum | None, Text, Form, Form(Multipart), JSON |
| Body (body) | unknown | Request payload (format depends on Body Type) |
| Headers (headers) | object | HTTP headers |
| Cookies (cookies) | object | HTTP cookies |
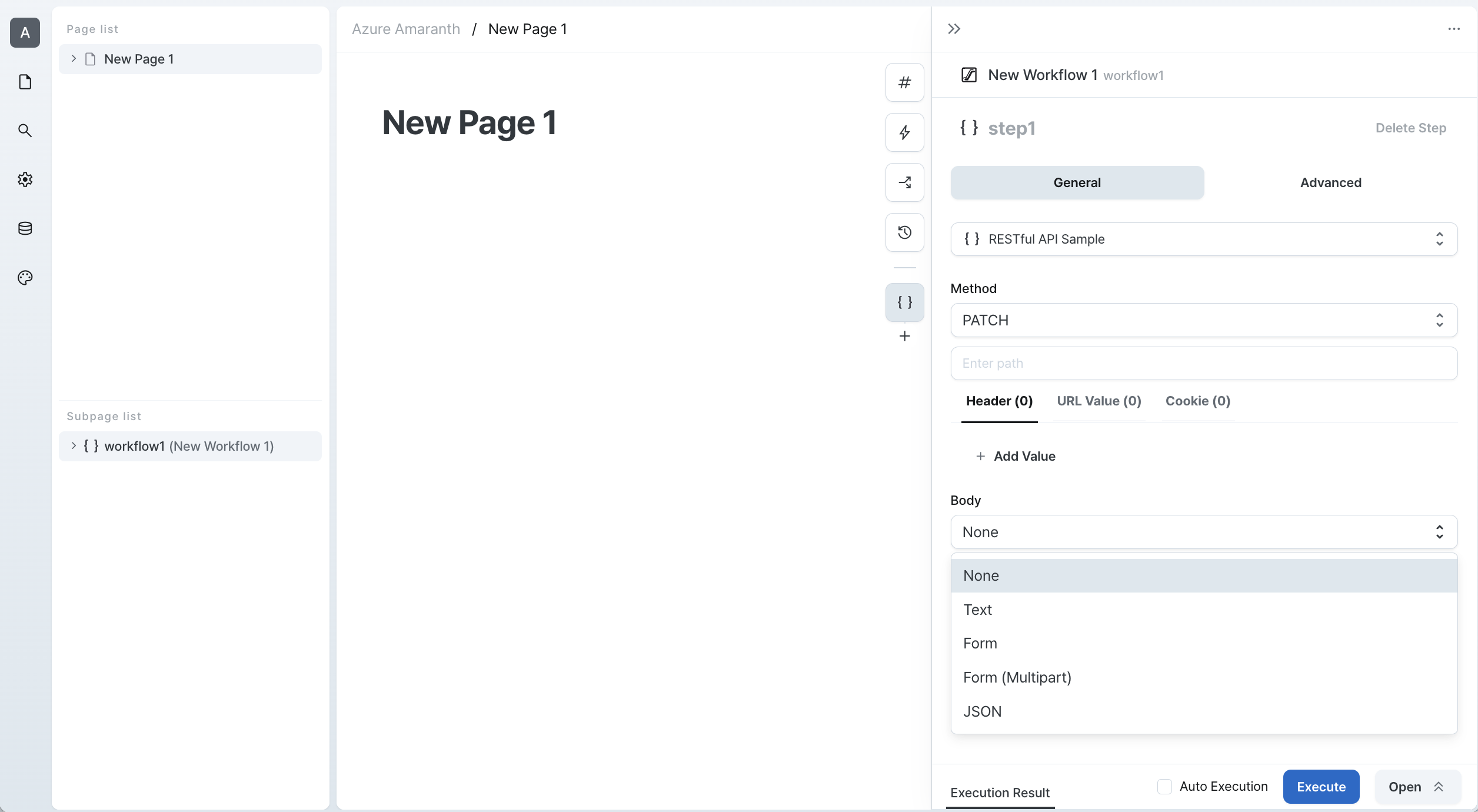
PATCH
PATCH requests are used to partially modify existing resources. Here's how to use PATCH requests:
- Specify the API endpoint URL
- Include the resource identifier in the URL
- Configure URL parameters if needed
- Select the appropriate body format
- Add any required authentication
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Path (path) | string | API endpoint URL |
| URL Parameters (params) | object | Dynamic URL values |
| Body Type | enum | None, Text, Form, Form(Multipart), JSON |
| Body (body) | unknown | Request payload (format depends on Body Type) |
| Headers (headers) | object | HTTP headers |
| Cookies (cookies) | object | HTTP cookies |
Working with Responses
When your API request completes, the response will be returned in the format specified by the API provider. Each API defines its own:
- Response format (JSON, XML, etc.)
- Data structure and field names
- Status codes and error handling
Always refer to your API's documentation to properly handle responses.
Response Example
// Response example
{
status: 200,
statusText: 'OK',
data: {
id: 123,
name: 'Hops Kang',
email: 'hops@example.com',
createdAt: '2024-01-01T00:00:00Z'
},
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'x-request-id': 'abc123'
}
}
// Use the response
return outputs.data.name;